The Walls of the Alimentary Canal Have Four
Oesophagus enters the stomach at an acute angle. The bony pelvis is composed of four bones.

Wall Of The Alimentary Canal Flashcards Quizlet
Arrange them in order from the.
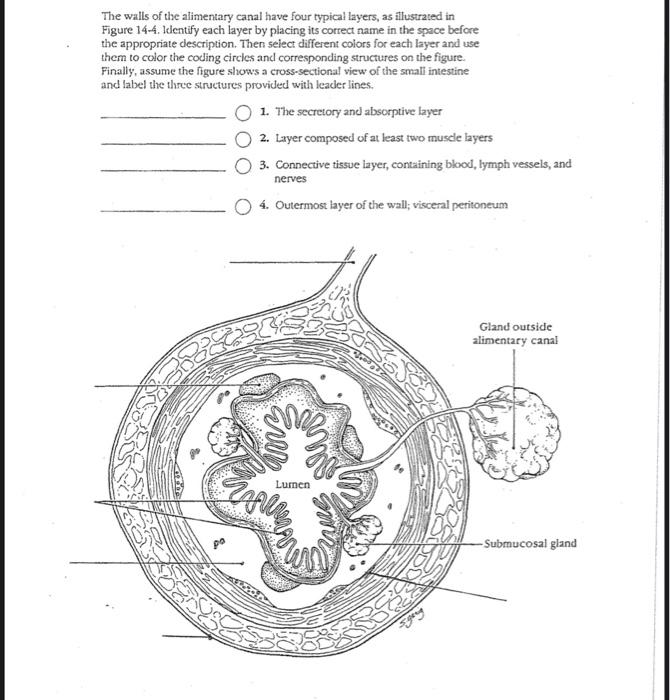
. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. From the esophagus to the anal canal the walls of every organ of the alimentary canal are made up of the same four basic layers. Alimentary canal performs the function of digesting food.
The cells of the exocrine glands are foveolar chief cells and parietal cellsThe other type of gastric gland is the pyloric gland. The walls of the stomach are made up of four layers. Which layer of the alimentary canal is constructed from either stratified squamous or simple columnar epithelium.
It breaks it down to smaller pieces and aids in the absorption of the digested food. Name the four ABO blood. Four layers of digestive tract walls.
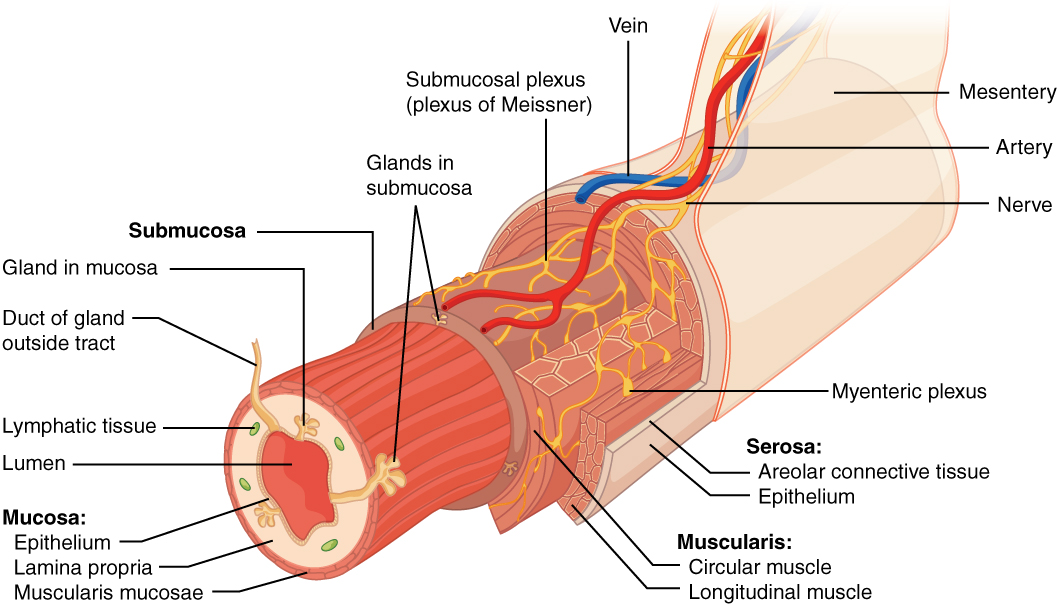
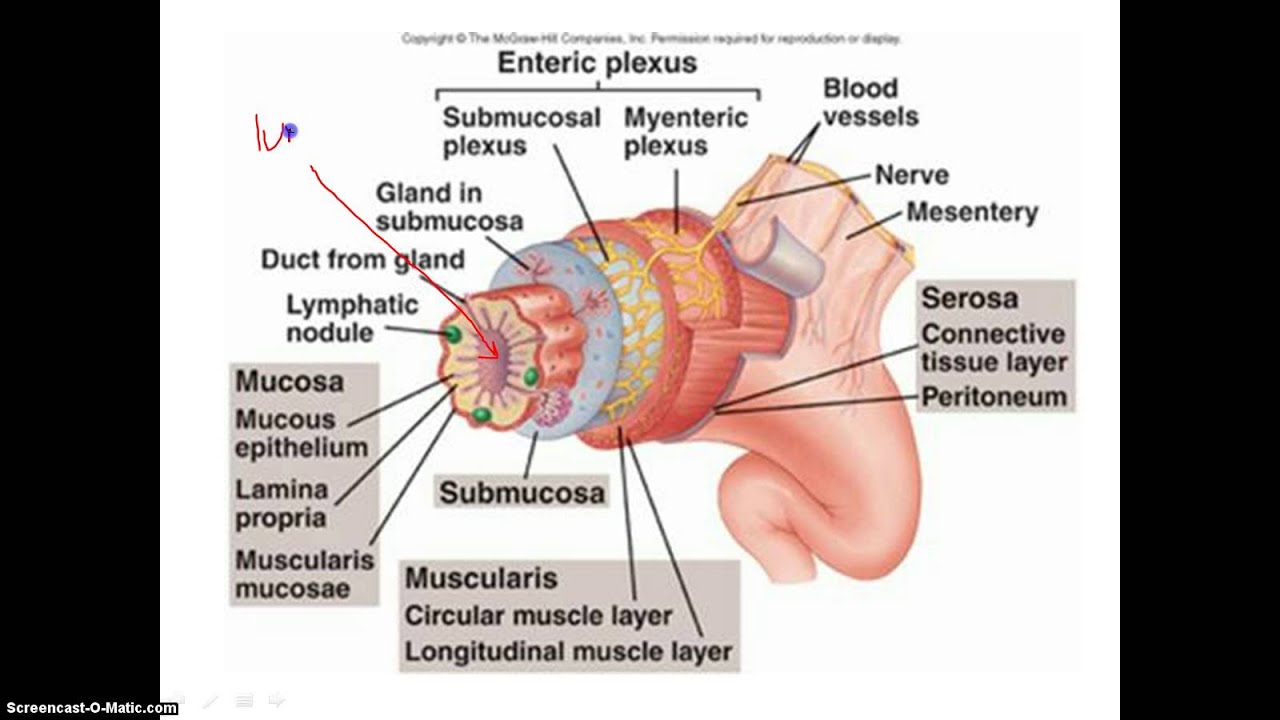
Smooth muscle tissues help in peristalsis to move food up and down the alimentary canal. It is made of. The walls of the alimentary canal from the esophagus to the anal canal have the same four tissue layers Figure 2.
Their axons are extended from the dorsal root ganglia to the grey matter of the central nervous system. Cells of the alimentary canal and multicellular consisting of cluster of cells salivary gland. Going from the inside out these are.
Walls of the intra-abdominal section of the oesophagus are compressed when there is a positive intra-abdominal pressure. The mouth has a total of eight four upper and four lower premolars. Apart from the alimentary canal there are numerous vital accessory organs that assist your body digest food but the food doesnt pass through them.
Ruminants are organisms that have four stomachs the reticulum rumen omasum and abomasum. See alimentary canal. In addition to the alimentary canal there are several important accessory organs that help your body to digest food but do not have food pass through them.
Accessory organs of the digestive system include the teeth tongue salivary glands liver gallbladder and pancreas. The sheep alimentary canal digestive system has evolved to developing microbial flora micro-organisms. Two hip bones which form the anterior and lateral walls.
Gastric glands are mostly exocrine glands and are all located beneath the gastric pits within the gastric mucosathe mucous membrane of the stomach. -The walls have windows that allow small proteins to pass through but not cells. They are mostly located in the blood vessel walls like arteries and veins urinary tract trachea and digestive system.
This is accomplished by enzymes through hydrolysis. Teeth tongue salivary glands liver gallbladder and pancreas are some of the digestive systems accessory organs. The wall of the stomach is made of the same four layers as most of the rest of the alimentary canal but with adaptations to the mucosa and muscularis for the unique functions of this organ.
The gastric mucosa is pitted with innumerable gastric pits which each house 3-5 gastric glands. The many enzymes involved in chemical digestion are summarized in Table 1. The mucosa is the innermost layer.
From inside to outside Mucosa muscularis mucosa submucosa and muscularis externa. The sphincter is classified as a physiological or functional sphincter as it does not have any specific sphincteric muscle. Instead the sphincter is maintained by four factors.
Walls of the digestive tract have four concentric layers. Finally we have the molars which are the most posterior teeth found in the mouth with six on the top and six on the bottom. Sacrumand coccyx which form the posterior wall.
Gene flow The movement of genetic material between populations. In mobile animals gene flow generally occurs as individuals emigrate immigrate or breed with individuals from other populations. These four bones are connected by four joints and lined by four muscles.
These are involuntary and non-striated in nature and have tapered ends. In biology tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organA tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. The bony pelvis with its joints and muscles form a strong basin-shaped structure with multiple foramina The pelvis contains and protects the lower.
Gene The sequence of base pairs within a molecule of DNA that codes for one specific protein. Cardiac Muscle Tissues. Schematic drawing of the digestive tract layers Mucosa.
The visceral sensory fibres have their cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia and their dendrites lie in the organs which are not under voluntary control like the heart blood vessels different parts of the alimentary canal. Large food molecules for example proteins lipids nucleic acids and starches must be broken down into subunits that are small enough to be absorbed by the lining of the alimentary canal. In addition to the typical circular and longitudinal smooth muscle layers the muscularis has an inner oblique smooth muscle layer Figure 2342.
On the basis of the mode of pouring of their secretions glands are divided into two categories namely exocrine and endocrine glands. In fact most such layers occur in the hollow organs of the respiratory urinary and reproductive systems as well. The English word tissue derives from the French word tissu the past.
These majorly consist of making up the. Exocrine glands secrete mucus saliva earwax oil milk digestive enzymes and other cell products. Sheep are herbivorous ruminants for that digest coarse fibrous plants to obtain the required amount of nutrients.

Solved The Walls Of The Alimentary Canal Have Four Typical Chegg Com

Layers Of The Alimentary Canal Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
0 Response to "The Walls of the Alimentary Canal Have Four"
Post a Comment